How to Choose the Right Trunnion Ball Valve for Your Application
When selecting the appropriate trunnion ball valve for a specific application, several critical factors must be taken into account to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Industry expert Dr. John Smith, a renowned valve technology specialist, emphasizes that “choosing the right trunnion ball valve is not just about the valve itself, but understanding the unique demands of your system.” This highlights the necessity for a comprehensive assessment of the operational environment, including pressure, temperature, and media being handled.
Trunnion ball valves, known for their robust construction and ability to handle higher pressures, are commonly used in various sectors, including oil and gas, chemical processing, and water treatment. It is essential to match the valve characteristics with the intended application to prevent leaks, reduce maintenance costs, and enhance safety. Factors such as valve size, material compatibility, and sealing mechanism should be meticulously evaluated.
In conclusion, understanding the specific requirements of your application and consulting with industry experts can lead to the effective selection of a trunnion ball valve. By making informed decisions, organizations can achieve enhanced operational efficiency and longevity in their valve systems.

Understanding Trunnion Ball Valves and Their Functionality
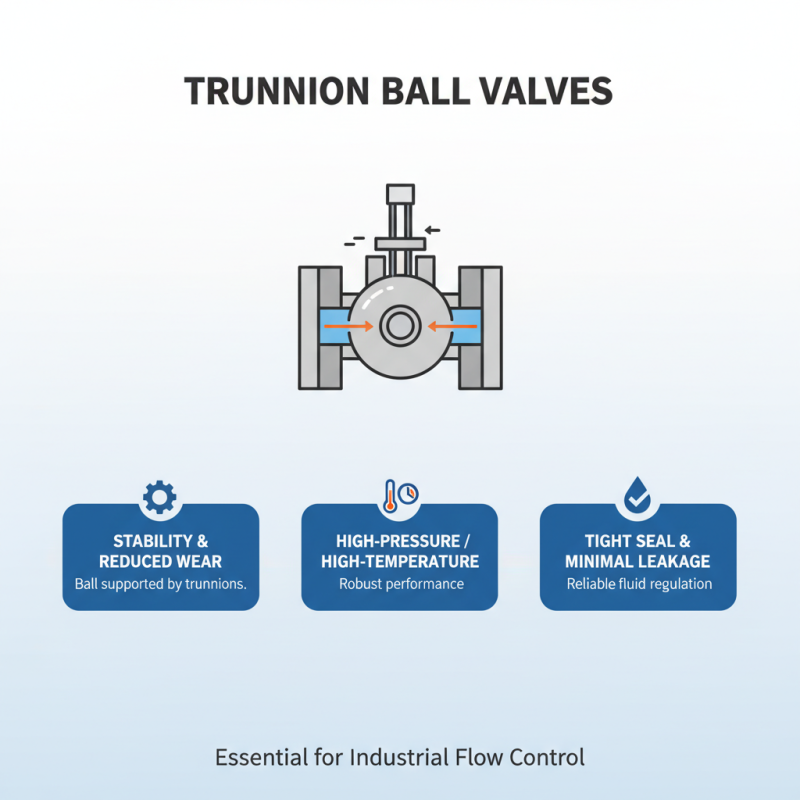
Trunnion ball valves are crucial components in many industries, known for their reliable performance in regulating fluid flow. These valves are designed with a ball supported by trunnions, which allows for greater stability and reduces the wear from mechanical stress. Their functionality is particularly advantageous in high-pressure and high-temperature applications, ensuring a tight seal and minimal leakage.
When choosing a trunnion ball valve, consider the media type, pressure rating, and temperature requirements of your system. It's essential to assess the valve's connection types, such as flanged or welded, to ensure compatibility with your piping. Additionally, the materials used in valve construction should match the fluid characteristics to avoid corrosion or degradation over time.
Tips: Always consult with an expert or refer to performance data sheets to ensure the valve meets your operational demands. Regular maintenance checks can help prolong the lifespan of the valve and maintain its functionality. Finally, consider the actuator options, as choosing the right actuator can enhance control and efficiency in your system.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Trunnion Ball Valve
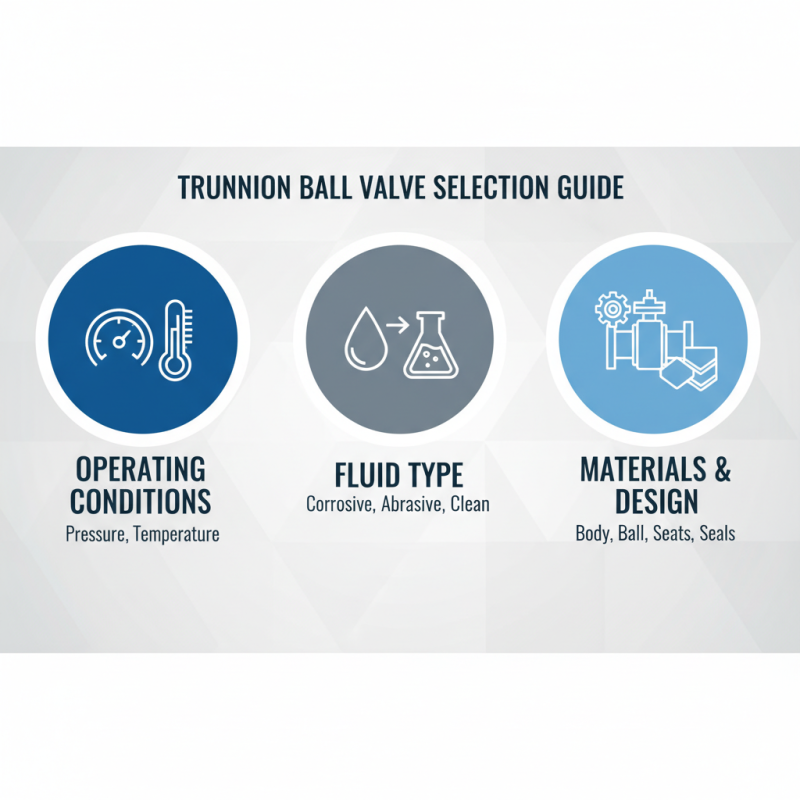
When selecting a trunnion ball valve for your specific application, several key factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and reliability. First and foremost, understanding the operating conditions is vital. Factors such as pressure, temperature, and the type of fluid being controlled can drastically influence the valve's suitability. It's essential to ensure that the valve’s design and material can withstand the specific conditions of your system, including any potential corrosive elements present in the fluids.
Another important consideration is the valve’s size and connection type. The valve must match the pipeline specifications to ensure a tight seal and proper flow. Additionally, evaluating the actuating mechanism is crucial, as it impacts the ease of operation and control accuracy. Depending on the complexity of the system, you might choose between manual, electric, or pneumatic actuators, each offering different benefits based on speed and automation. By carefully assessing these factors, you can choose a trunnion ball valve that meets both your performance requirements and operational needs.
Material Selection for Trunnion Ball Valves Based on Application Needs
When selecting the appropriate trunnion ball valve for specific applications, material choice plays a critical role in ensuring optimal performance and longevity. The primary materials used for trunnion ball valves include stainless steel, carbon steel, and special alloys. Each of these materials has unique properties that make them suitable for different operational conditions. For instance, stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion and often chosen for applications involving corrosive media or environments, making it ideal for chemical processing industries. On the other hand, carbon steel is a cost-effective option commonly used in less corrosive environments but may require coatings to enhance its resistance.
In addition to the chemical compatibility, temperature and pressure ratings are vital considerations in material selection. Valves operating at high temperatures may require materials with excellent thermal stability, such as Inconel or other high-temperature alloys. Conversely, applications with extreme pressure might necessitate reinforced materials that can withstand stress without compromising integrity. Moreover, when dealing with abrasive substances, materials such as duplex stainless steel or hardfacing techniques may be employed to prolong service life. By understanding the specific demands of their applications, engineers can make informed decisions on the most suitable materials for trunnion ball valves, ultimately enhancing reliability and efficiency in their systems.
Evaluating Pressure and Temperature Ratings for Valve Selection
When selecting a trunnion ball valve for your specific application, understanding the pressure and temperature ratings is crucial. These ratings serve as the foundation for ensuring that the valve can withstand the operating conditions without risking failure or leaks.
Pressure ratings—typically represented in pounds per square inch (PSI)—indicate the maximum pressure the valve can handle. It's essential to match this with the pressure encountered in your system to ensure safe and efficient operation. In high-pressure applications, selecting a valve rated for slightly above the expected operating pressure is advisable to accommodate any pressure surges that might occur.
Temperature ratings play an equally important role in valve selection. Every material used in the construction of a valve has a temperature limit, beyond which the integrity of the valve can be compromised.
Therefore, it’s important to consider not only the normal operating temperature but also any potential extremes that may occur during operation. It’s advisable to consult the manufacturer's specifications to ensure that the valve's material and design can handle the operating temperatures, including both the maximum and minimum thresholds.
By carefully evaluating these parameters, you can select a trunnion ball valve that is capable of performing reliably under the conditions it will face in your system.
Common Applications of Trunnion Ball Valves in Various Industries
Trunnion ball valves are increasingly recognized for their reliability and efficiency in various industrial applications. One of the most common uses for these valves is in the oil and gas sector. According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), this industry requires valves that can withstand high pressures and temperatures, making trunnion ball valves ideal for upstream, midstream, and downstream operations. Their design ensures a tight seal, reducing the risk of leaks and enhancing safety in hazardous environments.
In the chemical processing industry, trunnion ball valves are favored for their ability to handle corrosive media. A recent study by the Chemical Engineering Magazine indicates that the demand for robust and durable valves has surged by over 20% in recent years, driven by the need for improved efficiency and safety standards. The trunnion design provides mechanical stability, which is critical when dealing with aggressive chemicals. Moreover, their quarter-turn operation simplifies the management of flow control in intricate piping systems, vital for maintaining optimal process conditions.
Another notable application is in the water treatment sector. As highlighted in a report by the American Water Works Association (AWWA), trunnion ball valves facilitate effective flow regulation during the filtration and disinfection processes. Their ability to manage high flow rates with minimal pressure loss helps in maintaining the quality of treated water. The versatility and reliability of trunnion ball valves position them as essential components across these industries, adapting easily to various operational demands while ensuring compliance with stringent safety and environmental regulations.
Related Posts
-
Top Benefits of Trunnion Mounted Ball Valves in 2025 for Industrial Applications
-
Understanding the Essential Role of Trunnion Valves in Modern Industrial Applications
-

10 Best Ball and Globe Valves for Optimal Fluid Control in Industrial Applications
-

Top 5 Forged Valves: Best Options for Reliability and Performance
-

Top 10 Ball Valves for Industrial Applications You Should Consider
-

Top 5 Pressure Valves: Choosing the Best for Your Industrial Needs
